Kidney Stones vs UTI: How to Identify and Treat Each Problem Effectively
Kidney Stones vs UTI: How to Identify and Treat Each Problem Effectively
Blog Article
A Comparative Study of the Danger Variables and Avoidance Strategies for Kidney Stones and Urinary System Infections: Insights for Better Wellness
The raising occurrence of kidney stones and urinary system infections (UTIs) requires a closer examination of their interrelated danger aspects and prevention methods. By determining and addressing these shared susceptabilities, we can establish much more effective techniques to minimize the threats associated with each. Kidney Stones vs UTI.
Summary of Kidney stones
Kidney stones are an usual urological condition, impacting around 10% of people eventually in their lives. These solid mineral and salt deposits form in the kidneys when pee ends up being concentrated, enabling minerals to take shape and bind with each other. The structure of kidney stones differs, with calcium oxalate stones being one of the most widespread, complied with by uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones.
Danger factors for the growth of kidney stones include dehydration, nutritional routines, obesity, and specific clinical problems such as hyperparathyroidism or metabolic problems. Signs and symptoms of kidney stones can vary from mild discomfort to severe discomfort, often providing as flank pain, hematuria, and urinary necessity.

Understanding Urinary System Tract Infections
Urinary system infections (UTIs) stand for a widespread medical problem, particularly among women, with roughly 50-60% experiencing a minimum of one UTI in their life time - Kidney Stones vs UTI. UTIs happen when germs enter the urinary system system, bring about inflammation and infection. This condition can influence any type of part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, with the bladder being the most typically impacted website
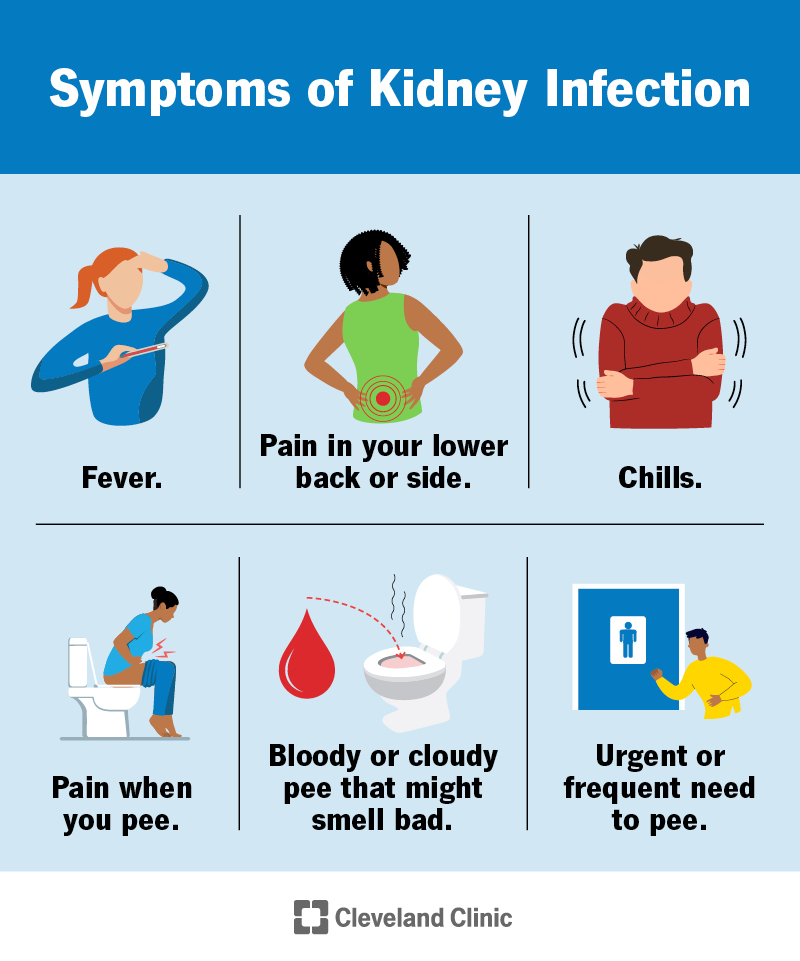
The scientific presentation of UTIs normally includes signs and symptoms such as dysuria, raised urinary frequency, seriousness, and suprapubic pain. In many cases, clients may experience systemic signs such as fever and chills, suggesting an extra extreme infection, potentially including the kidneys. Diagnosis is primarily based on the presence of signs, affirmed by urinalysis and pee culture to determine the causative microorganisms.
Escherichia coli is the most usual virus related to UTIs, accounting for around 80-90% of cases. Danger variables consist of anatomical proneness, sex-related task, and specific medical problems, such as diabetic issues. Understanding the pathophysiology, scientific indications, and analysis requirements of UTIs is critical for effective administration and avoidance methods in at risk populaces.
Shared Danger Elements
A number of shared danger aspects add to the advancement of both kidney stones and urinary system system infections (UTIs), highlighting the interconnectedness of these two conditions. Dehydration is a noticeable risk variable; insufficient liquid intake can bring about concentrated urine, promoting the development of kidney stones and producing a beneficial environment for bacterial growth, which can precipitate UTIs.
Hormone aspects, specifically in ladies, may also offer as shared danger factors. Adjustments in estrogen levels can impact urinary system system health and stone formation. Additionally, obesity has been recognized as an usual threat variable, where excess weight can bring about metabolic modifications that favor both kidney stone development and urinary system infections. Identifying these shared threat variables is vital for understanding the complicated partnership between these two health concerns.
Avoidance Approaches
Recognizing the shared threat aspects for kidney stones and urinary system system infections emphasizes the relevance of implementing effective avoidance approaches. Central to these techniques is the promotion of sufficient hydration, as enough fluid consumption weakens urine, minimizing the concentration of stone-forming materials and lessening the danger of infection. Health care specialists commonly advise drinking at the very least 2 to 3 litres of water daily, customized to individual demands.
Additionally, dietary alterations play an important duty. A balanced diet low in sodium, oxalates, and animal proteins can minimize the development of kidney stones, while enhancing the consumption of veggies and fruits sustains urinary system health. Normal surveillance of urinary system pH and composition can additionally assist in recognizing predispositions to stone development or infections.
Furthermore, maintaining appropriate health practices is crucial, particularly in females, to protect against urinary system tract infections. This includes wiping from front to back and urinating after intercourse. Last but not least, for people with reoccurring concerns, prophylactic treatments or medicines may be necessary, guided by health care specialists, to resolve details risk factors successfully. Overall, these prevention techniques are crucial for reducing the occurrence of both kidney stones and urinary system infections.
Way Of Life Modifications for Health
Applying certain way of life changes can dramatically reduce the risk of establishing kidney stones and urinary system infections (UTIs) A well balanced diet plan plays a crucial role; boosting liquid intake, specifically water, can thin down urine and help avoid stone development as well as flush out germs that might lead to UTIs.
Routine exercise is also vital, as it advertises overall wellness and aids reference in preserving a healthy and balanced weight, additional lowering the danger of metabolic problems related to kidney stones. Additionally, practicing excellent hygiene is vital in protecting against UTIs, particularly in ladies, where wiping methods and post-coital urination can play precautionary duties.
Avoiding excessive high levels of caffeine and alcohol, both of which can aggravate dehydration, is suggested. Finally, routine clinical exams can help check kidney function and urinary wellness, identifying any very early signs of problems. By embracing these way of life adjustments, individuals can boost their overall health while efficiently decreasing the risk of kidney stones and urinary system tract infections.
Final Thought
Finally, the comparative evaluation of kidney stones and urinary system infections emphasizes the value of common danger factors such as dehydration, nutritional habits, and weight problems. Applying website link reliable avoidance strategies that focus on adequate hydration, a well balanced diet plan, and regular exercise can alleviate the occurrence of both problems. By attending to these typical determinants through lifestyle adjustments and boosted hygiene methods, people can improve their total wellness and reduce their susceptability to these widespread health problems.
The increasing prevalence of kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) requires a closer examination of their interrelated danger variables and prevention methods - Kidney Stones vs UTI. The structure of kidney stones varies, with calcium oxalate stones being the most common, adhered to by uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones
Treatment options vary based on the size and kind of the stone, varying from conventional management with raised fluid consumption to clinical treatment like lithotripsy or medical elimination for larger stones. Furthermore, obesity has been determined as an usual risk factor, where excess weight can lead to metabolic adjustments that prefer both kidney stone development and urinary system system infections.Understanding the shared danger variables for kidney stones and urinary system infections highlights the relevance of applying effective prevention strategies.
Report this page